As citizen science continues to flourish across diverse scientific disciplines, it is crucial to take a step back, and scrutinize variations across initiatives, to account for their respective strengths and weaknesses in attracting diverse societal segments and their effectiveness in mobilizing citizens with assorted motivations
On 31 July 2023, Nature’s Scientific Reports published a research article titled “Demographic and Motivational Differences Between Participants in Analog and Digital Citizen Science Projects for Monitoring Mosquitoes”. This article presents an exhaustive analysis of two prominent mosquito monitoring initiatives: Mückenatlas (MS) and our very own Mosquito Alert (MA). The study stands out in its unique approach of contrasting two projects that, while aligned in their overarching goals, vastly differ in task presentation and communication strategy.
Significant differences emerged in the demographic structure of the two projects. MA notably attracted more female participants, a rarity and a significant stride in citizen science. It also appealed more to the younger demographic. These variations could be attributed to user-friendly nature of the MA app, age-related barriers to technology, and divergent public health concern among participants. Delving into their motivations and sentiments provided further clarity.
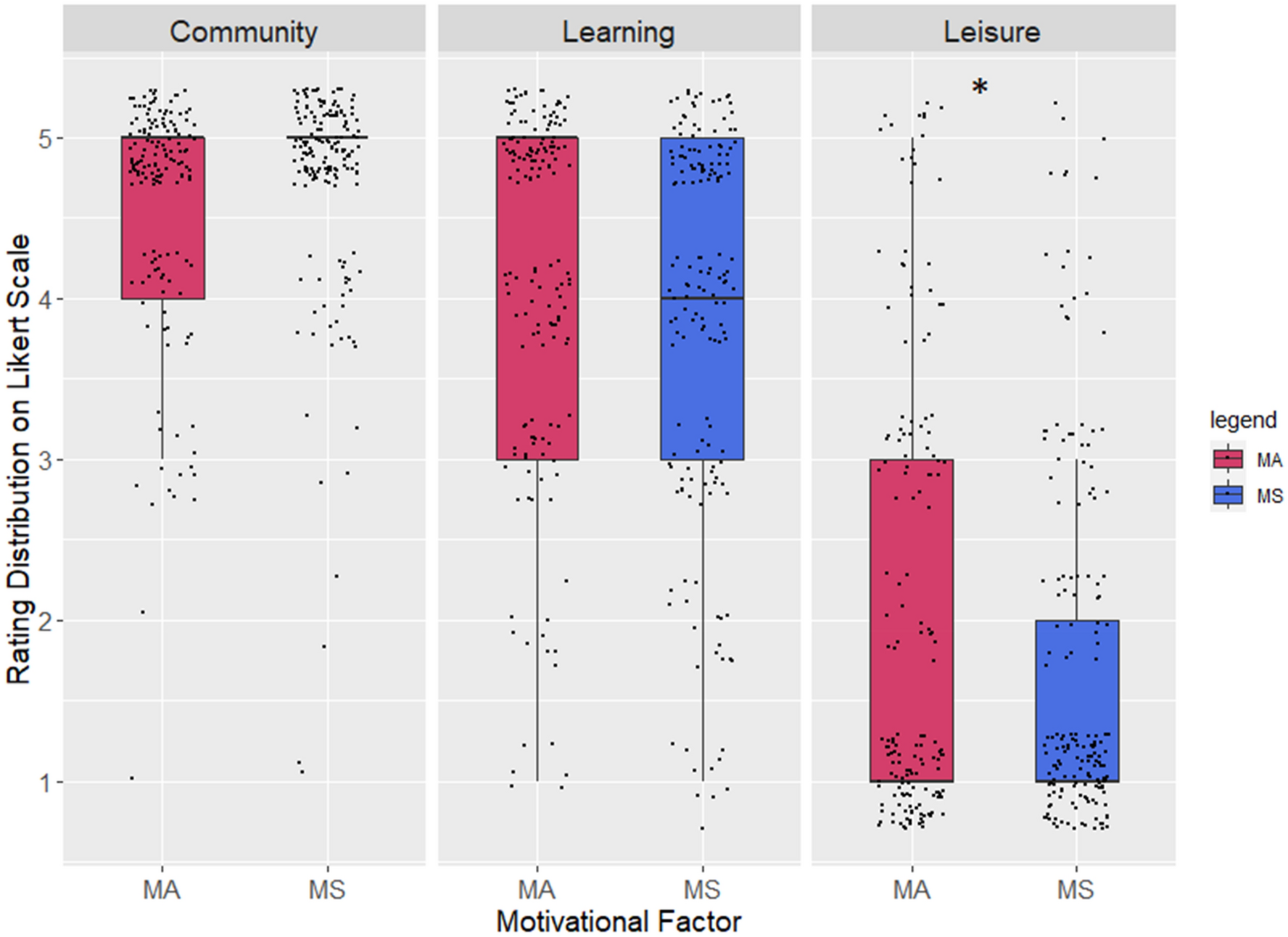
Figure 1. Distribution of ratings for motivational factors as reasons for participation
While both projects demonstrated that supporting research and community engagement were key drivers for involvement, in-depth sentiment analysis revealed stark contrasts. MA cohort exhibited motivations rooted in external factors, showcasing a dominant desire for security and a focus on mosquito control.
These discrepancies have been attributed to the differing communication strategies employed by each project. Whereas focus on early warning and surveillance of invasive mosquito species may attract those keen on preventing negative outcomes, the positive aspects of understanding mosquito diversity can be appealing to an entirely different audience.
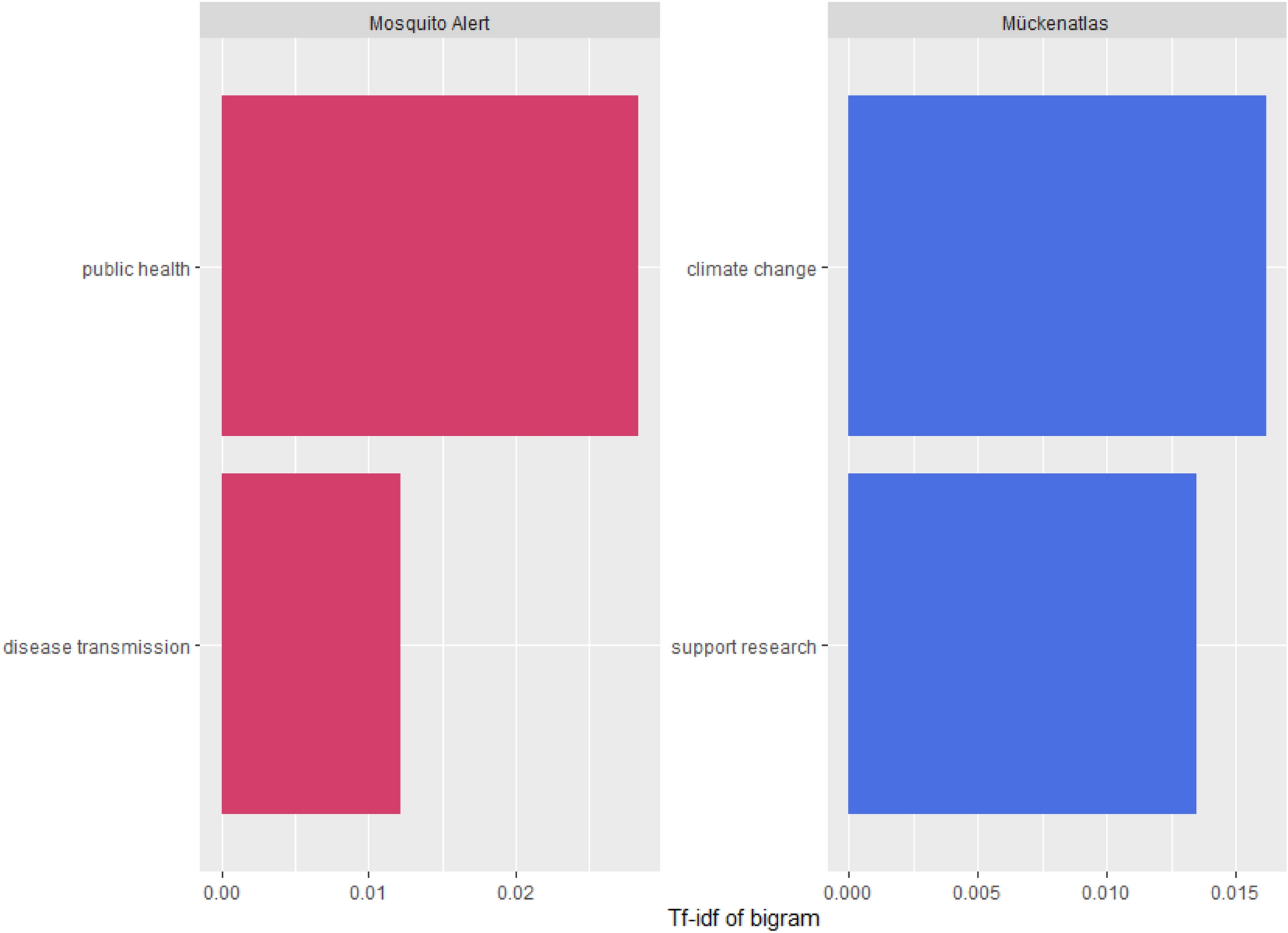
Figure 2. Answer motivation responses of each project.
Exploring the diversity of backgrounds, motivations, and sentiments of participants—particularly in projects with aligned goals—has yielded invaluable insights. Nuanced adjustments in project design and communication strategies, can substantially sway participant engagement. The contrast between online accessibility and a field-based approach broadens the scope for community involvement. At the same time, it initiates a critical conversation on finding the optimal equilibrium between streamlining participation and nurturing scientific curiosity.
This research underscores the importance of in-depth analysis. As the world of citizen science continues to evolve, these insights pave the way for more inclusive, effective, and engaging projects, contributing to the collective effort of understanding and managing our natural world.
Author: Berj Dekramanjian
References: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-023-38656-y